JPY Market Update
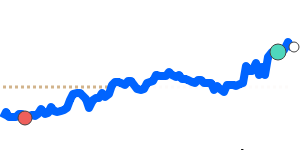
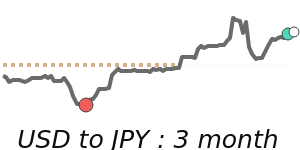
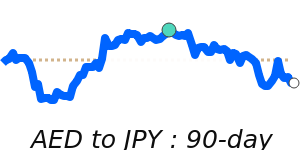
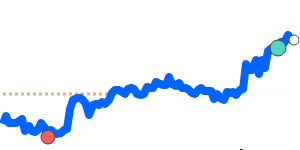
The Japanese Yen has seen a slight weakening against the US dollar, trading near its 30-day low of around 0.006303, which is about 1.5% below its three-month average. This decline is linked to rising regional tensions in the Middle East, especially the recent escalation involving Iran, which increased global uncertainty. As a result, investors continue to seek safe-haven assets, but the Yen's recent softness suggests cautious sentiment as geopolitical risks weigh.
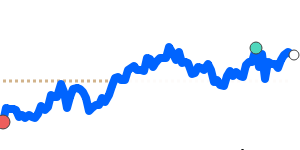
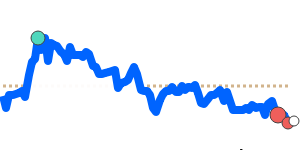
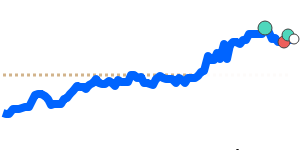
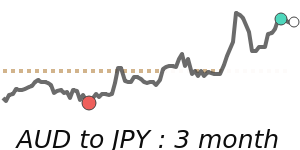
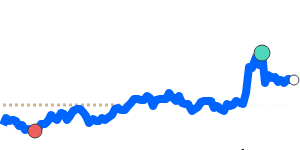
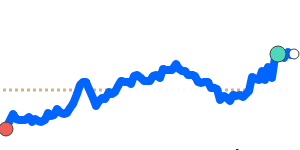
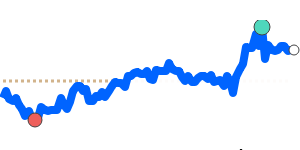
Meanwhile, against the Euro, the Yen remains relatively steady, trading just above its recent three-month average at 0.005473. Its stability against EUR and GBP reflects balanced market conditions, with limited volatility in these pairs. However, the Yen has weakened further against the Australian dollar and Canadian dollar, trading around 3% below their three-month averages, at approximately 0.009043 and 0.008570 respectively. This decline is partly prompted by regional growth concerns and broad risk sentiment shifts.
Overall, the Yen's movement reflects recent geopolitical tensions and cautious market positioning. While it remains stable in some major pairs, the currency's slight softness against the USD underscores ongoing cautious sentiment amid global uncertainties.