CHF Market Update
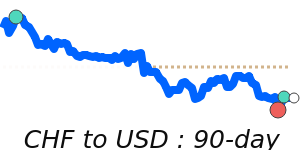
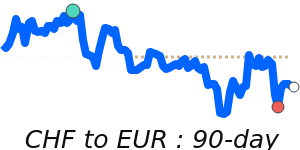
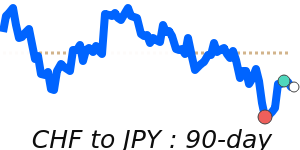
The Swiss franc remains somewhat supported amid ongoing geopolitical uncertainties, which boost its safe-haven appeal. Recently, the CHF has gained ground against the euro, trade at around 1.1061, slightly above its 3-month average, reflecting increased demand for stability. Against the US dollar, it sits near 1.2843, just a touch above its recent average, showing a stable but cautious tone. The CHF also strengthened against the yen, trading near 203.2, a 7-day high and about 1.9% above its 3-month average, driven by risk-averse sentiment.
However, the Swiss National Bank continues to signal readiness to step into the market if the franc's strength threatens to impact exports. With low inflation and steady economic growth forecasts around 1%, the SNB's stance remains cautious, aiming to manage the currency’s strength without immediate rate changes.
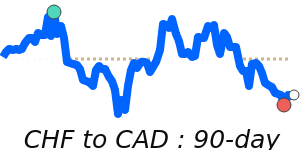
Meanwhile, the Swiss franc is near recent lows against the Australian dollar, trading at about 1.8040, and at 1.7443 versus the Canadian dollar. These moves show a slight shift as traders balance safe-haven flows with central bank interventions. Overall, the franc’s movements reflect both its safe-haven status and ongoing efforts by the SNB to keep its value in check.