MXN Market Update
12 Mar 2026 • 03:42 GMT
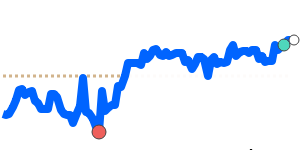
The Mexican Peso has seen notable swings recently, largely influenced by changes in global risk sentiment. After strengthening and falling to about 17.56 against the US dollar earlier this week, the peso weakened again to around 17.72 amid rising geopolitical tensions in the Middle East. This pattern underscores the peso's sensitivity to external risks.
On the currency front, the MXN/USD rate is roughly in line with its longer-term average, trading slightly below 0.05635. These moves highlight a cautious market stance as investors weigh the potential impact of geopolitical instability and economic policies. Similarly, against the euro and yen, the peso remains stable within recent ranges, though it has dipped closer to its 3-month lows against the Australian dollar, which is now near 0.07902.
Looking ahead, market focus will stay on global political developments and Mexico's inflation outlook. Expectations of future rate cuts from Banxico and rising oil prices could continue to pressure the peso downward, especially if risk aversion persists. Overall, expect continued volatility as market conditions evolve.