MYR Market Update
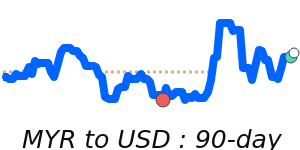
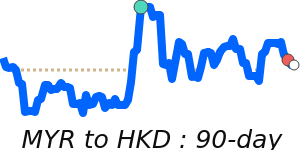
The Malaysian ringgit continues to hold firm against major currencies, driven by Malaysia's resilient economy and strong investments. Recently, the MYR has reached its highest levels since May 2018 against the US dollar, trading near 7.9680, which is about 1.9% above its three-month average. This strength is supported by optimism around Malaysia's role in the global AI supply chain and increased foreign interest in Malaysian assets, including government bonds.
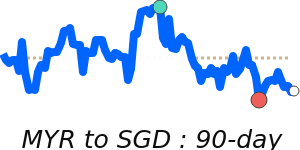
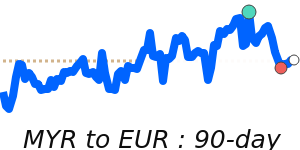
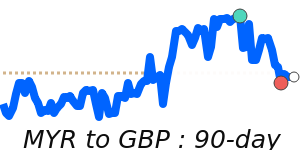
Against the euro, the MYR hit 90-day highs near 0.2212, up 3.7% from recent averages, reflecting positive economic sentiment and stable export demand. The currency also reached 7-day highs against the pound, trading near 0.1908, and against the Japanese yen, approaching 40.63, both indicating broad-based strength.
While the ringgit remains robust, its slight gains are steady rather than volatile. Malaysia's steady economic outlook, alongside cautious policies from Bank Negara Malaysia, suggest this strength may persist amid ongoing global uncertainties. Overall, the MYR's performance highlights Malaysia's resilience in a challenging global environment.