AUD Market Update
14 Mar 2026 • 01:15 GMT
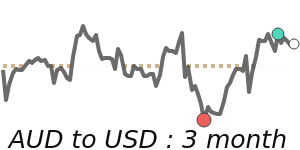
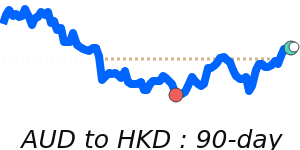
The Australian dollar remains slightly above its 3-month average, trading around 0.6990 against the USD, which is about 1.6% higher. However, momentum is limited as the USD gains strength from geopolitical tensions in the Middle East and rising energy prices. The AUD has struggled to break past the key 0.7000 mark, despite recent volatility within an 8.3% range from 0.6604 to 0.7152.
Market watchers note the Reserve Bank of Australia's hawkish signals and ongoing domestic inflation as factors supporting the AUD. Yet, geopolitical uncertainties and USD safe-haven flows keep the currency in a cautious stance. Some analysts see the AUD potentially moving toward the mid-70s US cents within the next few months, while others warn that the top may have been reached for now.
Overall, expect continued volatility in the AUD/USD, with the currency likely to trade within the broader range for the near term. Market dynamics remain sensitive to global geopolitical developments, energy prices, and domestic economic data.
📊 Quick forecast view
Near-term bias: 🔴 Mild downside
Expected range: 0.6990 – 0.7150
Dominant driver: 🌍 Global risk sentiment
3-month trend: 🟢 Uptrend