Outlook
CHF remains bid as a safe-haven amid global tensions, leaving it firmer vs peers. The SNB keeps 0% to protect inflation and exports. Markets expect vigilance on FX and possible intervention if the franc rallies too far. Risk appetite shifts could ease the bid.
Key drivers
- Safe-haven demand from tensions underpins CHF strength.
- SNB's 0% policy balances inflation risk with exporters.
- SNB can intervene if the franc rises too fast.
- 2025 tariff shock exposed export exposure and policy risk.
Range
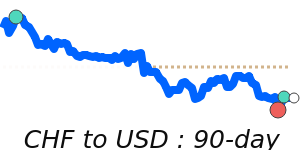
CHF/USD: current 1.2997; 3m avg 1.2709; range 1.2392–1.3115
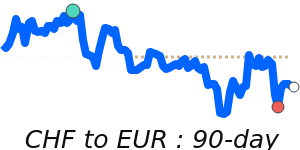
CHF/EUR: current 1.0997; 3m avg 1.0813; range 1.0648–1.1009
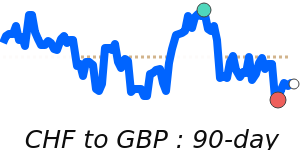
CHF/GBP: current 0.9639; 3m avg 0.9422; range 0.9298–0.9652
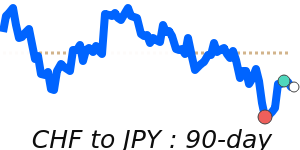
CHF/JPY: current 202.8; 3m avg 198.2; range 193.0–203.4
What could change it
- A shift in global growth or risk environment toward stability could ease CHF strength.
- Unexpected SNB policy shift or new currency action.
- Trade tensions escalate or ease, affecting risk demand.
- Switzerland’s export outlook or tariff policy developments.