Outlook
The euro remains choppy as Russia-Ukraine tensions and thin data flow keep trades range-bound. An expected improvement in German consumer confidence in March could lift EUR modestly, but final German GDP figures and Eurozone inflation prints could swing the currency if they surprise. The ECB’s cautious stance, with the deposit rate at 2.00%, supports limited upside unless inflation cools faster than expected. Longer-term positives include Bulgaria’s adoption of the euro (January 2026) and progress on the digital euro, which may underpin resilience. Elevated oil around $71 a barrel reinforces a higher energy-cost backdrop and could pressure the euro if inflation remains sticky. Overall, near-term dynamics point to range-trading with moves driven by data surprises and policy signals.
Key drivers
- Russia-Ukraine conflict dynamics and energy supply concerns; sanctions and geopolitical risk can shift risk sentiment and euro demand.
- ECB policy stance and the 2.00% deposit rate; policy communication and inflation trajectory remain pivotal.
- Upcoming German data: consumer confidence in March, final German GDP, and Eurozone inflation readings; deviations from estimates can move EUR.
- Eurozone enlargement and reform efforts, notably Bulgaria joining the euro area in 2026, supporting longer-term euro credibility.
- Digital euro developments; progress toward a potential issuance by 2029 could influence long-run euro dynamics.
- Oil prices and energy costs; stable to higher oil supports inflation risk, which can weigh on the euro if not offset by weaker inflation.
- Global risk sentiment and USD direction; EUR tends to be sensitive to broad market moves and carry trade dynamics.
Range
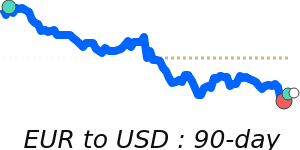
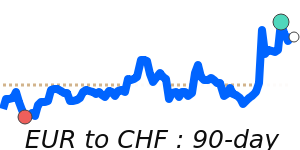
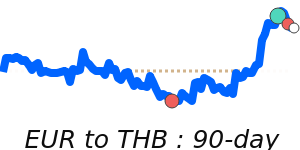
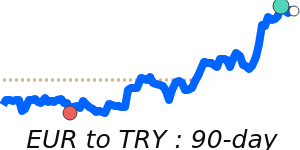
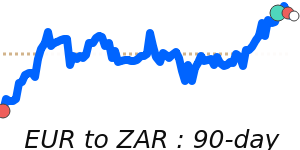
EURUSD at 1.1776, just above its 3-month average, having traded in a very stable 3.8% range from 1.1586 to 1.2031.
EURGBP at 0.8724, near its 3-month average, having moved in a stable 2.0% range from 0.8628 to 0.8799.
EURJPY at 183.6, near its 3-month average, trading in a very stable 3.2% range from 180.5 to 186.2.
Oil (Brent Crude OIL/USD) at 71.03, 9.9% above its 3-month average of 64.61, with a wide 21.5% range from 59.04 to 71.76.
What could change it
- Data surprises: stronger or weaker German GDP, inflation, or consumer confidence data than expected.
- ECB policy shifts or new guidance that alters rate expectations or inflation outlook.
- Geopolitical developments in Russia/Ukraine or fresh sanctions that alter energy markets and risk sentiment.
- Oil price moves; a sharp decline could relieve inflation pressures and support EUR, while spikes could weigh on it.
- Accelerated euro-area reforms or further expansion news (e.g., continued euro adoption) and progress on the digital euro.