Outlook
The zloty looks set to stay firm vs the dollar and euro as the NBP keeps policy steady and growth remains solid. Domestic political risk and external shocks could trim gains if risk appetite wanes.
Key drivers
- NBP pause at 4.00% supports the zloty.
- Inflation easing toward target reinforces the policy stance.
- IMF growth outlook and rapid EU fund disbursement bolster Poland’s trajectory.
- Political divisions within the ruling coalition add fiscal policy risk.
- UBS sees the zloty holding firm vs euro and dollar through 2026 due to robust fundamentals.
Range
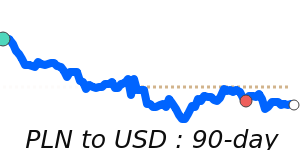
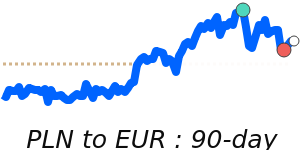
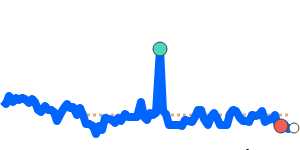
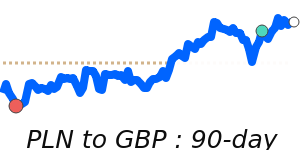
PLN/USD 0.2720; Range 0.2708–0.2867. PLN/EUR 0.2340; Range 0.2331–0.2383. PLN/GBP 0.2029; Range 0.2027–0.2084. PLN/JPY 42.92; Range 42.70–44.33.
What could change it
- A clearer shift in NBP policy (further cuts or hikes).
- Inflation surprises (hotter or cooler than target).
- Major political developments or fiscal policy changes.
- External risk appetite moves altering demand for Polish assets.