USD Market Update
13 Mar 2026 • 00:22 GMT
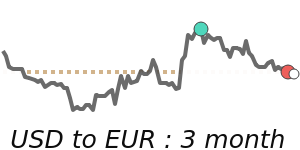
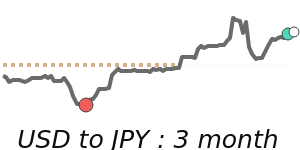
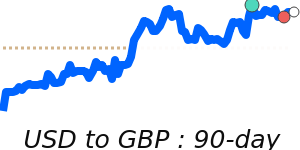
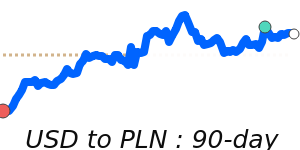
The US dollar remains strong, driven by ongoing geopolitical tensions in the Middle East and rising oil prices, which encourage safe-haven buying. Against the euro, the USD stands at around 0.8680, about 1.9% above its recent 3-month average, reflecting increased demand amid global uncertainties. Similarly, against the Japanese yen, the USD is trading near 159.2, which is nearly 1.9% higher than its average over the past quarter. The dollar's recent strength is also supported by safe-haven flows, despite some mixed U.S. economic data, such as weaker job growth.
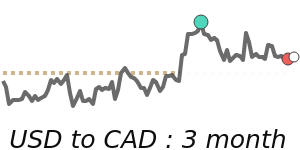
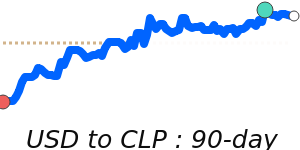
In contrast, the Australian dollar has weakened further and is trading around 1.4131, about 2.8% below its three-month average, amid higher energy prices and uncertain global risk appetite. Meanwhile, the US dollar remains close to its usual range against the Canadian dollar and Swiss franc, with little major movement noted.
Markets are attentive to upcoming U.S. inflation data, which could influence the Fed’s future rate decisions. For now, the dollar's strength appears constructive but may face some softening if geopolitical tensions ease or if the U.S. signals a pause in rate hikes.
USDEUR Near-term bias: 🟢 Mild upside
Expected range: 0.8540 – 0.8690
Dominant driver: 🌍 Global risk sentiment
3-month trend: ⚪ Range-bound